Wendy's - statistics & facts
Key insights
- Revenue of the Wendy's Company worldwide
- 2.1bn USD

Detailed statistics
Revenue of Wendy's worldwide 2009-2023
- Consumer spending in the QSR sector in the U.S.
- 320.3bn USD

Detailed statistics
Consumer spending in the quick service restaurant sector in the U.S. 2004-2023
- Number of QSRs in the U.S.
- 198.1k

Detailed statistics
Number of quick service restaurants in the U.S. 2011-2022
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Current statistics on this topic
Related topics
Recommended statistics
Industry overview
4
- Premium Statistic Global quick service restaurant industry market size 2022-2023
- Premium Statistic Consumer spending in the quick service restaurant sector in the U.S. 2004-2023
- Premium Statistic Sales of leading quick service restaurant chains in the U.S. in 2022
- Premium Statistic Leading quick service restaurant chains in the U.S. in 2022, by number of units
Industry overview
-
Premium Statistic
Global quick service restaurant industry market size 2022-2023

Global quick service restaurant industry market size 2022-2023
Market size of the quick service restaurant industry worldwide in 2022 and 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Consumer spending in the quick service restaurant sector in the U.S. 2004-2023

Consumer spending in the quick service restaurant sector in the U.S. 2004-2023
Consumer spending in the quick service restaurant (QSR) sector in the United States from 2004 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Sales of leading quick service restaurant chains in the U.S. in 2022

Sales of leading quick service restaurant chains in the U.S. in 2022
Leading quick service restaurant (QSR) chains in the United States in 2022, by systemwide sales (in billion U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Leading quick service restaurant chains in the U.S. in 2022, by number of units

Leading quick service restaurant chains in the U.S. in 2022, by number of units
Leading quick service restaurant (QSR) chains in the United States in 2022, by number of units
Company information
8
- Premium Statistic Revenue of Wendy's worldwide 2009-2023
- Premium Statistic Revenue of Wendy's globally 2015-2023, by segment
- Premium Statistic Operating income of Wendy's 2009-2023
- Basic Statistic Net income of Wendy's 2009-2023
- Premium Statistic Total assets of Wendy's 2009-2023
- Premium Statistic Average global sales per unit of Wendy's 2017-2023, by segment
- Premium Statistic Cost of sales of Wendy's 2009-2023, by segment
- Premium Statistic Initial franchise investments for Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2023
Company information
-
Premium Statistic
Revenue of Wendy's worldwide 2009-2023

Revenue of Wendy's worldwide 2009-2023
Revenue of the Wendy's Company worldwide from 2009 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Revenue of Wendy's globally 2015-2023, by segment

Revenue of Wendy's globally 2015-2023, by segment
Revenue of the Wendy's Company worldwide from 2015 to 2023, by segment (in million U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Operating income of Wendy's 2009-2023

Operating income of Wendy's 2009-2023
Operating income of the Wendy's Company worldwide from 2009 to 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
-
Basic Statistic
Net income of Wendy's 2009-2023

Net income of Wendy's 2009-2023
Net income of the Wendy's Company worldwide from 2009 to 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Total assets of Wendy's 2009-2023

Total assets of Wendy's 2009-2023
Total assets of the Wendy's Company worldwide from 2009 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Average global sales per unit of Wendy's 2017-2023, by segment

Average global sales per unit of Wendy's 2017-2023, by segment
Wendy's average worldwide sales per unit from 2017 to 2023, by segment (in thousand U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Cost of sales of Wendy's 2009-2023, by segment

Cost of sales of Wendy's 2009-2023, by segment
Cost of sales of the Wendy's Company worldwide from 2009 to 2023, by segment (in million U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Initial franchise investments for Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2023

Initial franchise investments for Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2023
Initial franchise investments for Wendy's restaurants in the United States in 2023 (in U.S. dollars)
Units and employment
-
Premium Statistic
Number of Wendy's restaurants worldwide 2011-2023, by mode of operation

Number of Wendy's restaurants worldwide 2011-2023, by mode of operation
Number of Wendy's restaurants worldwide from 2011 to 2023, by mode of operation
-
Premium Statistic
Number of Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2011-2023, by mode of operation

Number of Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2011-2023, by mode of operation
Number of Wendy's restaurants in the United States from 2011 to 2023, by mode of operation
-
Premium Statistic
Number of Wendy's employees worldwide 2013-2023, by type

Number of Wendy's employees worldwide 2013-2023, by type
Number of Wendy's employees worldwide from 2013 to 2023, by type
Brand perception
6
- Premium Statistic Ad funds revenue of Wendy's 2018-2022
- Premium Statistic Wendy’s brand profile in the United States 2023
- Basic Statistic American Customer Satisfaction Index: Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2000-2023
- Premium Statistic Customer service in Wendy's drive-thrus in the U.S. 2022
- Premium Statistic Drive-thru order accuracy in selected U.S. restaurant chains 2022
- Premium Statistic Fastest drive-thru times in selected U.S. restaurant chains 2022
Brand perception
-
Premium Statistic
Ad funds revenue of Wendy's 2018-2022

Ad funds revenue of Wendy's 2018-2022
Advertising funds revenue of the Wendy's Company from 2018 to 2022 (in million U.S. dollars)
-
Premium Statistic
Wendy’s brand profile in the United States 2023

Wendy’s brand profile in the United States 2023
Wendy’s brand awareness, usage, popularity, loyalty, and buzz among restaurant chain customers in the United States in 2023
-
Basic Statistic
American Customer Satisfaction Index: Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2000-2023

American Customer Satisfaction Index: Wendy's restaurants in the U.S. 2000-2023
American Customer Satisfaction Index scores of Wendy's restaurants in the United States from 2000 to 2023
-
Premium Statistic
Customer service in Wendy's drive-thrus in the U.S. 2022
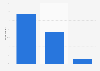
Customer service in Wendy's drive-thrus in the U.S. 2022
Employee customer service in Wendy's drive-thrus in the United States as of July 2022
-
Premium Statistic
Drive-thru order accuracy in selected U.S. restaurant chains 2022

Drive-thru order accuracy in selected U.S. restaurant chains 2022
Drive-thru order accuracy in selected restaurant chains in the United States as of July 2022
-
Premium Statistic
Fastest drive-thru times in selected U.S. restaurant chains 2022

Fastest drive-thru times in selected U.S. restaurant chains 2022
Fastest drive-thru times in selected restaurant chains in the United States as of July 2022 (in seconds)
Further reportsGet the best reports to understand your industry
Get the best reports to understand your industry
Contact


Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)


