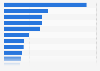
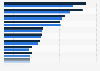
Use and demand growth in the past decades
Natural gas has a wide range of uses. It is a primary source for heating and electricity generation and a major feedstock for chemical products such as fertilizers and plastics. Due to it having a lower carbon content than other fossil fuels, natural gas advocates have promoted its use as a bridge fuel in the energy transition. As a result, governments of large-scale energy consumers such as Germany and the United States are building up gas-fired power capacity to reduce reliance on coal. This growth in demand is also reflected by the steady increase in global natural gas production, which rose by some 60 percent since the late 1990s. Global natural gas consumption closely mirrors production levels, and in 2022 amounted to 3.94 trillion cubic meters.Leading suppliers and surging costs
The U.S. is the world's largest natural gas producer and also among the top exporters of gaseous state natural gas shipped via pipelines to neighboring Canada and Mexico.Costs for purchasing this commodity tend to be lower in producer countries. This is particularly noticeable when comparing monthly natural gas prices in the U.S. and Europe. People in Europe often pay twice as much for natural gas as U.S. residents, with the gap having widened tremendously during the 2021 energy supply shortage. The eyewatering surge in fuel prices was later exacerbated by the Russia-Ukraine war.