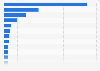
Global cumulative CO₂ emission shares by region 1750-2022
The distribution of regional cumulative carbon dioxide emissions has changed dramatically since 1750. For many decades the vast majority of emissions were produced in countries in Europe, specifically Great Britain, where the industrial revolution originated. As the United States began to emerge, the global distribution changed. By the start of the twentieth century, the United States accounted for almost a quarter of cumulative emissions, and by the 1950s its share had increased to almost 40 percent. With cumulative emissions of more than 400 billion metric tons of CO₂, the United States is now the biggest emitter in history.
China is now the second-biggest historical emitter, having seen its share of cumulative emissions grow from less than six percent in 1990 to more than 15 percent by the end of 2022.