Demographics
Brazil is highly urbanized despite its large size and it has the second highest urbanization rate of any country with over 100 million inhabitants (after Japan). The majority of the population live along coastal regions, especially to the east and south. Brazil's fertility rate has been below replacement level since the early 2000s, however its birth rate is still well above its death rate, suggesting continued population growth in the coming years. Historically, Brazil's net migration rate was negative, meaning the number of emigrants leaving was higher than the number of immigrants arriving. However, the 2010s marked a decade of consistently positive net migration, a large part of which was due to the influx of Venezuelan refugees who now make up the largest migrant group.Economy
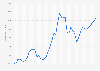
Brazil is also among the leading emerging countries, the so-called BRICS states (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa). Its gross domestic product (GDP) amounted to over 2.1 trillion U.S. dollars in 2023, making it one of the largest economies in the world. After several years of high growth rates, economic growth in Brazil stagnated in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but recovered with five percent growth in 2021. Brazil's exports (primarily commodities such as iron ore, petroleum, and agricultural goods) are worth over 330 billion U.S. dollars in 2022, and imported goods are valued at over 290 billion U.S. dollars, making it a net exporter of goods.Brazil's GDP per capita peaked in 2011, before falling significantly during the economic difficulties that followed the 2014 economic crisis, as well as during the pandemic - while the figure is expected to grow throughout the remainder of the 2020s, projections until 2028 still do not exceed 2011 levels. Brazil’s unemployment rate has also spiked throughout this period, although post-pandemic projections do show a decline. Similar trends in Brazil's inflation rate can also be observed over the past decade, with annual increases as high as nine percent in 2015 and 2022, although these are projected to fall to around three percent over the coming years.