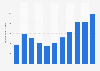
Merchandise and service imports
Mechanical and electronic products made up 40 percent of the country’s goods imports. In 2022, China’s major import products included integrated circuits, crude oil, and iron ore. China’s agricultural sector has been increasingly relying on imports in the last few years as well. China is the world’s largest importer of soybeans and meat and is among the leading importers of dairy, wine, and other food products and beverages.In terms of service trade, transportation-related service imports took up the largest share of all service imports in China in 2022. Since the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic, China’s travel imports have decreased drastically, as a travel ban was imposed. On the other hand, telecommunication, computer, and information services imports to China increased at a rapid pace.
China’s import partners
Impacted by the escalating economic and political conflicts with the western world, China continuously shifted its trade focus to Asia. As of 2022, China’s major import partners were the ASEAN countries, the European Union, Taiwan, and South Korea. Besides, China has been focusing on strengthening its trade relationship with the belt-and-road initiative countries as part of its new trade roadmap. As of 2022, 149 countries have signed the initiative, and the total import value from BRI countries reached nearly six trillion yuan.Nevertheless, thanks to the ease of the U.S.-China trade war, imports from the United States reached a historical high at around 154 billion U.S. dollars in 2022.
Despite an upward trend in China’s imports, the country’s exports surpass its imports by a wide margin, creating the largest merchandise trade surplus in the world. In 2022, China had a positive trade balance exceeding 877 billion U.S. dollars. However, in contrast to merchandise trade, trade in services show a constant deficit as service imports to China outperform exports by around 92 billion U.S. dollars annually.