
Daniel Slotta
Research expert covering Greater China

Detailed statistics
Smartphone mobile network subscriptions worldwide 2016-2028

Detailed statistics
Revenue of the smartphones industry worldwide 2019-2029

Detailed statistics
Global market share held by smartphone vendors 2012-2023

Global smartphone sales to end users 2007-2023
Number of smartphones sold to end users worldwide from 2007 to 2023 (in million units)

Smartphone revenues worldwide 2011-2023
Smartphone revenues worldwide from 2011 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)

Smartphone unit shipments worldwide 2007-2023, by vendor
Global smartphone shipments from 2007 to 2023, by vendor (in million units)

Number of cellular subscriptions China 2000-2022
Number of mobile cellular subscriptions in China from 2000 to 2022 (in millions)

Number of mobile subscriptions per 100 people in China 2007-2023
Number of mobile phone subscriptions per 100 inhabitants in China from 2007 to 2023

Number of mobile subscribers in China 2017-2023, by operator
Number of mobile subscribers in China from 2017 to 2023, by operator (in millions)

Number of smartphone users in China 2018-2027
Number of smartphone users in China from 2018 to 2022 with a forecast until 2027 (in millions)

Penetration rate of smartphones in China 2014-2029
Penetration rate of smartphones in China from 2014 to 2029

Production of cell phones by month in China 2020-2024
Production of cell phones in China from July 2020 to July 2024 (in million units)

Smartphone unit shipments in China 2012-2022
Total number of smartphone shipments in China from 2012 to 2022 (in million units)

Smartphone shipment volume in China Q1 2011-Q1 2024
Total number of smartphone shipments in China from 1st quarter 2011 to 1st quarter 2024 (in million units)

Smartphone shipments quarterly in China Q1 2014-Q3 2022, by vendor
Smartphone shipments in China from 1st quarter 2014 to 3rd quarter 2022, by vendor (in million units)

Shipment volume of foldable phones in China Q2 2022-Q2 2023
Number of foldable smartphone shipments in China from 2nd quarter of 2022 to 2nd quarter of 2023 (in 1,000s)

Smartphone vendor market share in China Q1 2014-Q1 2024
Vendors' market share of smartphone shipments in China from 1st quarter 2014 to 1st quarter 2024

Smartphone market share in China 2023, by leading model
Share of most popular smartphones sold in China in July 2023, by model

Market share held by smartphone OS in China 2023
Market share held by smartphone operating systems in China as of March 2023, by share of users

Share of mobile operating systems in China 2014-2023, by month
Market share of mobile operating systems in China from July 2014 to July 2023*

Brand distribution of 5G smartphones in use in China 2023
Brand distribution of 5G smartphones in use in China in 2023

Brand distribution of foldable phone brands in China 2022
Market share of companies that produce folding phones in China in 2022

Annual shipment volume of 5G smartphones in China 2019-2022
Number of 5G smartphones in China from 2019 to 2022 (in million units)

Share of 5G smartphone shipments in China 2022
5G smartphone share of total shipments in China from May 2021 toDecember 2022

Leading models of 5G smartphones in use in China 2022
Breakdown of most popular models of 5G smartphones in use in China in 2022

Penetration rate of 5G smartphones in China 2020-2021
Penetration rate of 5G smartphones in China in 2020 with an estimate for 2021
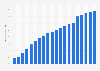
Official penetration rate of internet users in China 2014-H1 2024
Penetration rate of internet users in China published by the state from 2014 to June 2024

Penetration rate of mobile internet users in China 2014-2024
Penetration rate of mobile internet users in China from 2014 to 2024

Key figures of mobile app usage in China 2024
Key figures of mobile app usage in China as of May 2024

Leading apps in China 2024, by monthly active users
Monthly active users of the leading apps in China in February 2024 (in millions)

Daily mobile app usage in China Q4 2019-Q4 2023, by average number of hours
Average number of hours spent daily on mobile apps by users in China from 4th quarter 2019 to 4th quarter 2023


Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)