Global plastics industry - statistics & facts
Plastic production
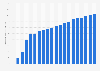
Annual global plastic production reached a high of 390.7 million metric tons in 2021, having experienced a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8 percent since 2009. In recent years, China has emerged as the leading producer of plastics, accounting for roughly 32 percent of global production. Despite the economic impacts of the pandemic, the production of plastic products in China has consistently produced around seven million metric tons of plastic products every month. In comparison, plastic production in Europe experienced a decline in 2020 before once again experiencing an increase to 57.2 million metric tons in 2021. North America (NAFTA) is the second-largest producer, with plastic production in the United States amounting to approximately 56.9 million metric tons in 2022.Plastics are versatile materials that are used in a wide range of products and applications. However, not all plastics are the same. There are approximately seven broader types of plastic that are produced and consumed in large quantities: polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene/styrofoam (PS), and miscellaneous plastics. Among them, polypropylene (PP) stands out with a production volume of 75.40 million metric tons in 2020, projected to reach 107.20 million metric tons by 2050. PP is a versatile plastic widely used in various industries, including automotive, packaging, textiles, and household goods. Its exceptional combination of properties, such as durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, makes it suitable for applications such as automotive parts, food packaging, and consumer products.