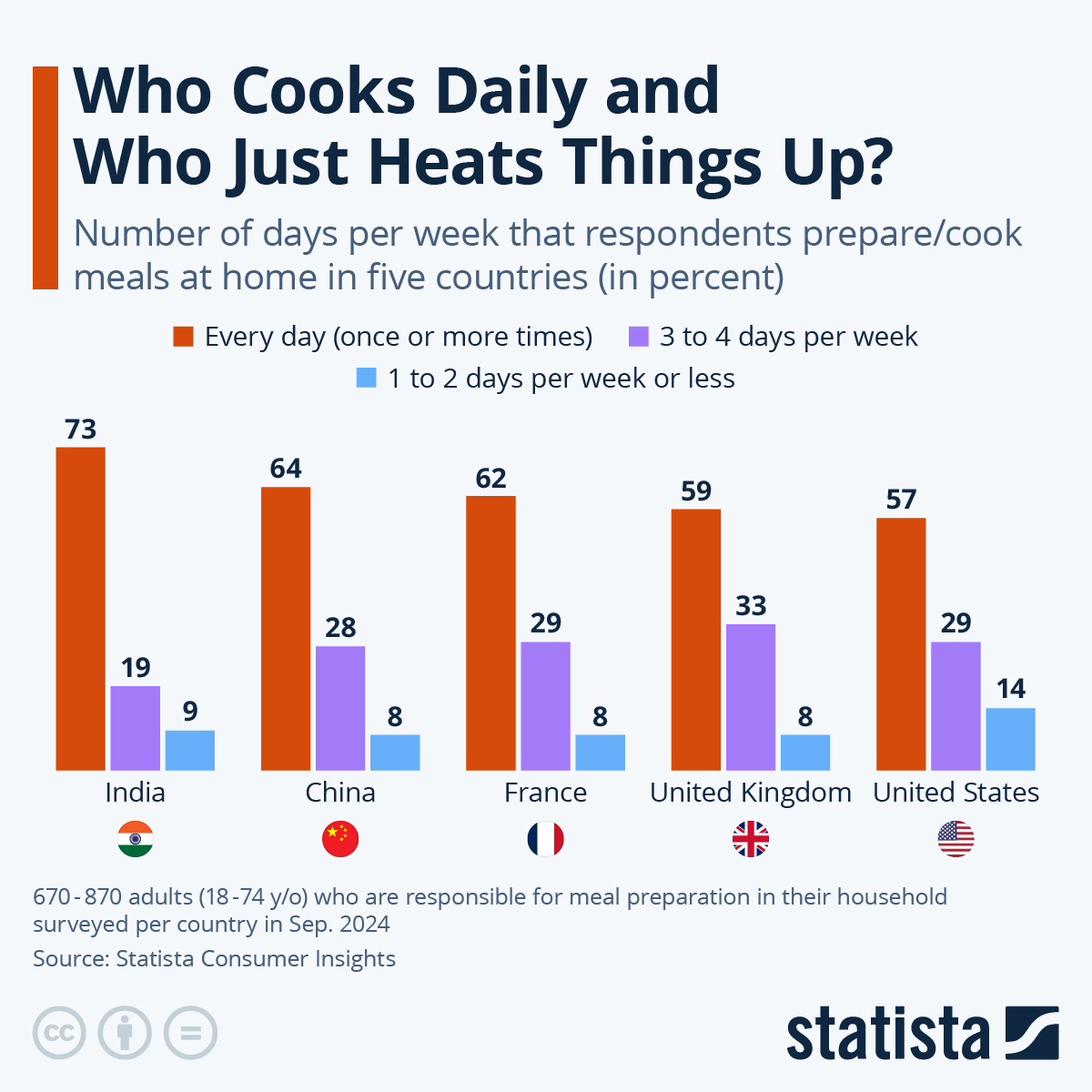
Around the world, daily cooking habits reflect cultural, economic and social differences. In the United States, for example, convenience often takes precedence: busy lifestyles and the prevalence of fast-food chains mean that many Americans tend to rely on takeout, out-of-home options or frozen meals. This trend is visible in the latest Statista Consumer Insights survey conducted in 2024 on eating behaviors. Among the eight countries studied, Americans are the least likely to cook/prepare homemade meals daily: 57 percent of respondents responsible for meal preparation in their household declared to do so, compared to 63 percent on average.
In France, the prevalence of daily home cooking is at 62 percent among those in charge of meals, while India records the highest rate of the survey: 73 percent. Generally, European and Asian consumers tend to remain more attached to culinary traditions and control over ingredients (e.g. fresh/regional products), though globalization, urbanization, new trends (e.g. food delivery, fast food) and change in lifestyles are slowly blurring these lines. For some populations, economic factors such as home cooking's cost efficiency also continue to play an important role in everyday practice.