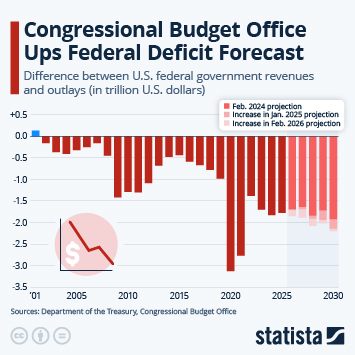
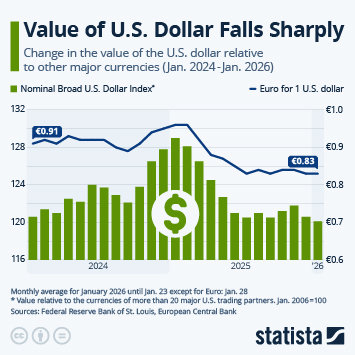
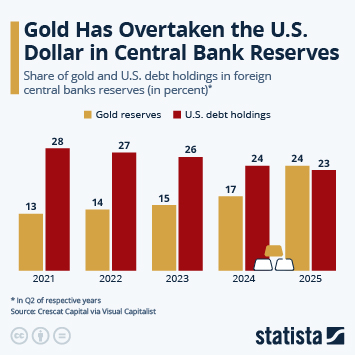
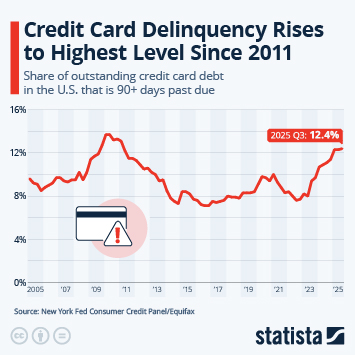
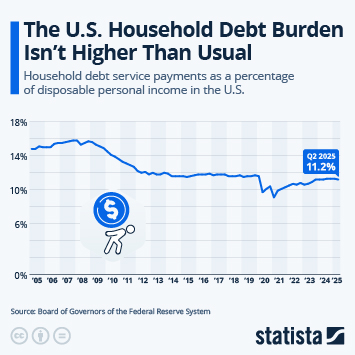
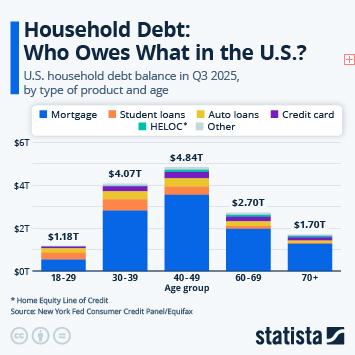
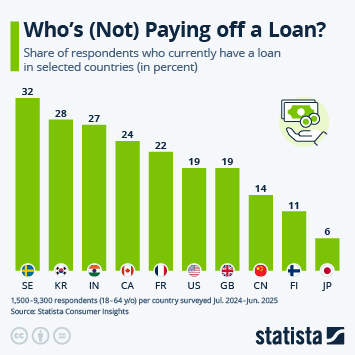
According to the latest data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), household debt in the United States amounted to around 69 percent of GDP in 2024. This ratio is higher than several other major economies (between 44 and 50 percent in Spain and Germany, respectively, 61 percent in France and 65 percent in Japan). In 2024, three countries had a household debt ratio in excess of 100 percent of GDP: Switzerland (125 percent) Australia (112 percent) and Canada (100 percent).
Over the past thirty years, the level of household debt in relation to GDP has risen considerably in high-income countries. For all eight economies analyzed in the following infographic, the average debt-to-GDP ratio has risen from 51 percent in 1990 to 72 percent in 2024. Many advanced economies, with the notable exception of Germany and Japan, experienced a sharp peak in household debt to GDP in the early 2000s. This excess of personal debt was one of the underlying causes of the global financial crisis of 2007-2008. Since then, household debt levels have tended to fall back in some countries, such as Spain and the United States, while in others they have risen again.