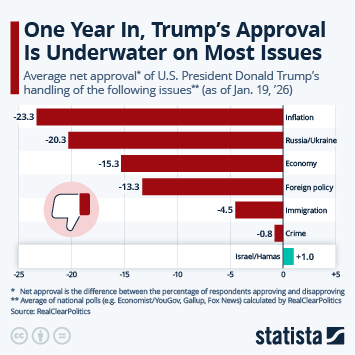
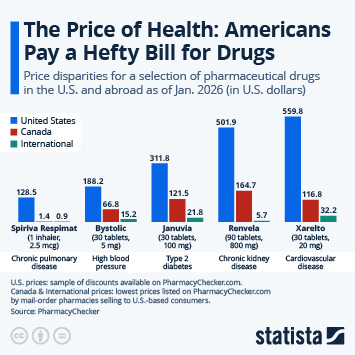
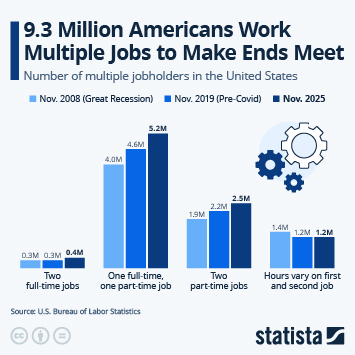
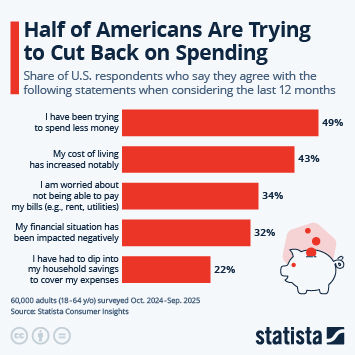
Despite the challenging economic environment and a high degree of uncertainty due to the shutdown-induced lack of economic data, the Fed remains cautiously optimistic in its latest economic outlook. In fact, Fed officials upped their GDP growth projection for 2026 by half a percentage point since September, even though very little data has come out since. The Federal Open Market Committee's median growth projection for 2026 is now 2.3 percent, up from 1.8 percent in September and just 1.6 percent in June.
For 2025, the FOMC is now predicting 1.7 percent growth, as we're still waiting for a first GDP growth estimate for Q3, which is now scheduled to be released on December 23. In Q1 2025, real GDP had contracted 0.6 percent, due to tariff frontloading resulting in a steep increase in imports, which is a subtraction in the calculation of GDP. In the second quarter, the opposite effect, i.e. a steep decline in imports due to tariffs, resulted in 3.8 percent growth, neither of both readings accurately reflecting the fundamental state of the economy.
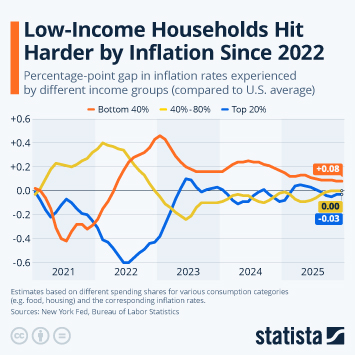
In terms of consumer prices, Fed officials now expect inflation to cool slightly quicker than previously anticipated, projecting 2.4 percent inflation in Q4 2026, compared to a previous estimate of 2.6 percent. By the end of 2027, they expect inflation to return to the Fed's target level of 2 percent. Looking at the labor market, FOMC members expect the unemployment rate to peak at 4.5 percent in Q4 2025 before gradually falling to 4.2 percent by 2027.